Gum Disease Explained: Risk Factors, Symptoms, Treatment And More!

Periodontitis, or gum disease, refers to infection of gums, which if not treated, can lead to tooth loss in adults. While periodontitis is common, it can be prevented and treated. It often is caused by poor oral hygiene. In this post, we are discussing gum disease risk factors, causes, and other aspects that matter.
Symptoms & causes
Patients with periodontitis may have swollen, red gums, which may feel tender when touched. Gums may be prone to bleeding, especially while brushing. Many patients also find pus in gums and may have a hard time chewing food. Other symptoms include receding gums. Periodontitis is mostly caused by plaque, and plaque, if untreated, can become tartar. Tartar cannot be removed with brushing and flossing alone, and it is absolutely necessary to see a dentist as soon as the first symptoms of gum diseases appears.
What are the risk factors for gum disease?
Poor oral hygiene and gingivitis are two common causes of gum disease. Smoking, chewing tobacco, and use of certain recreational drugs, marijuana can also increase the risks. In some cases, gum disease is triggered by a change in hormones, such as menopause. Risk factors also include vitamin C deficiency, obesity, and use of certain medications. Genetics may have a role in gum disease, according to some studies. Certain diseases, such as cancer, can impact gum health and cause certain diseases like gingivitis. Diabetic patients and those suffering from Crohn’s disease are also at a higher risk.
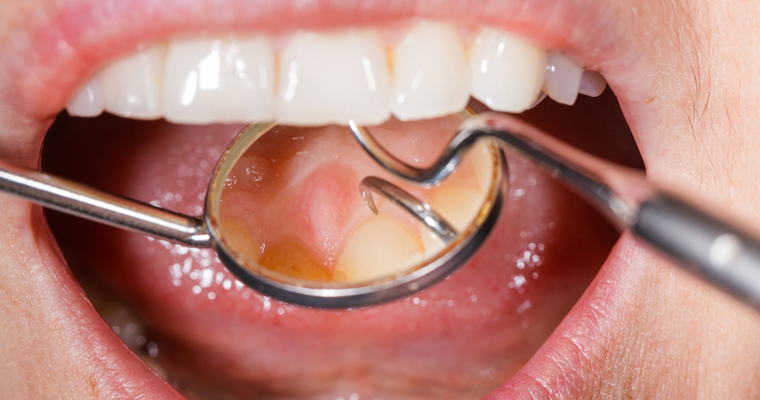
How is gum disease treated?
The entire periodontitis treatment depends on the extent of condition, and your dentist may recommend deep cleaning and scaling, which will remove tartar. Nonsurgical treatments may include use of antibiotics, which may help in controlling the infection caused by bacteria. Options like Root planning can be considered. In advanced cases, surgical treatments like bone grafting and pocket reduction surgery can be considered.
How to prevent gum disease?
Brushing and flossing regularly can prevent gum disease. Good oral hygiene and regular appointments with your dentist are two important aspects to consider. If you see first signs of gum disease, do not delay in going to the dentist. The good news is gum diseases can be reversed with early medical treatment and intervention. Ensure that you use toothpaste and oral products as recommended by your dentist, and schedule regular checkups at least once in six months.
Look for a dentist near you now!


 How to Choose the Right Stairlift Solution for Your Home
How to Choose the Right Stairlift Solution for Your Home  Basic First Aid for Fractures: Stabilizing the Injury
Basic First Aid for Fractures: Stabilizing the Injury  Sweet Treats and Convenient Picks: Navigating the World of Edibles and Disposables
Sweet Treats and Convenient Picks: Navigating the World of Edibles and Disposables  The Gut’s Tale: 5 Captivating Books to Dive Into
The Gut’s Tale: 5 Captivating Books to Dive Into  Top Tips To Help Keep You Looking Younger For Longer In Australia.
Top Tips To Help Keep You Looking Younger For Longer In Australia.  Is Bangkok a Good Place to Get LASIK
Is Bangkok a Good Place to Get LASIK  5 Situations Individuals Should Seek the Services of a Birmingham CPA
5 Situations Individuals Should Seek the Services of a Birmingham CPA  Life Without Teeth: Navigating Edentulism in Panama City Beach, FL
Life Without Teeth: Navigating Edentulism in Panama City Beach, FL  Should You Hire A CPA For Your Small Business?
Should You Hire A CPA For Your Small Business?  Boba Bonanza: Discovering the Delights of Bubble Tea Around the World
Boba Bonanza: Discovering the Delights of Bubble Tea Around the World